Our projects
PRIMED
It is the mission of the Pacific Regional Institute for Marine Energy Discovery (PRIMED) to accelerate the development and adoption of marine renewable energy technologies, including wind, wave, and tidal solutions. This is achieved by working with both communities and the private sector in order to identify the resources, assess the technology, and weigh the economics.
PRIMED’s aim is to act as the connective tissue between BC’s remote communities and marine renewable energy project developers. PRIMED provides second party assessment of MRE devices and we can help communities identify candidate technologies for their projects.
PRIMED is supported with funding from Pacific Economic Development Canada.
Energy Modelling Hub
EMH's mission is to support timely & evidence-based policymaking toward a net zero economy by bringing together public policy and energy modelling communities as maintaining and providing access to a comprehensive suite of robust and open-source resources and modelling tools. EMH is an independent modelling, data centre of reference and a dynamic community of practices helping Canadian energy policymakers chart an effective pathway to a decarbonised energy system.
Rebuild Initiative
Reducing energy use in existing buildings is key to avoiding catastrophic climate change. Better computer models of how our buildings are performing are needed to give robust design solutions and evidence-based policies. Data-driven methods that use machine-learning have great potential as our buildings provide lots of data, but little is currently used for reducing emissions. The ReBuild Initiative is an industry-government-academia consortium that will undertake 16 projects that encompass the breadth and complexity of the challenge, each co-designed with a partner organization to apply specific areas of research to meet their needs.
Solid Carbon
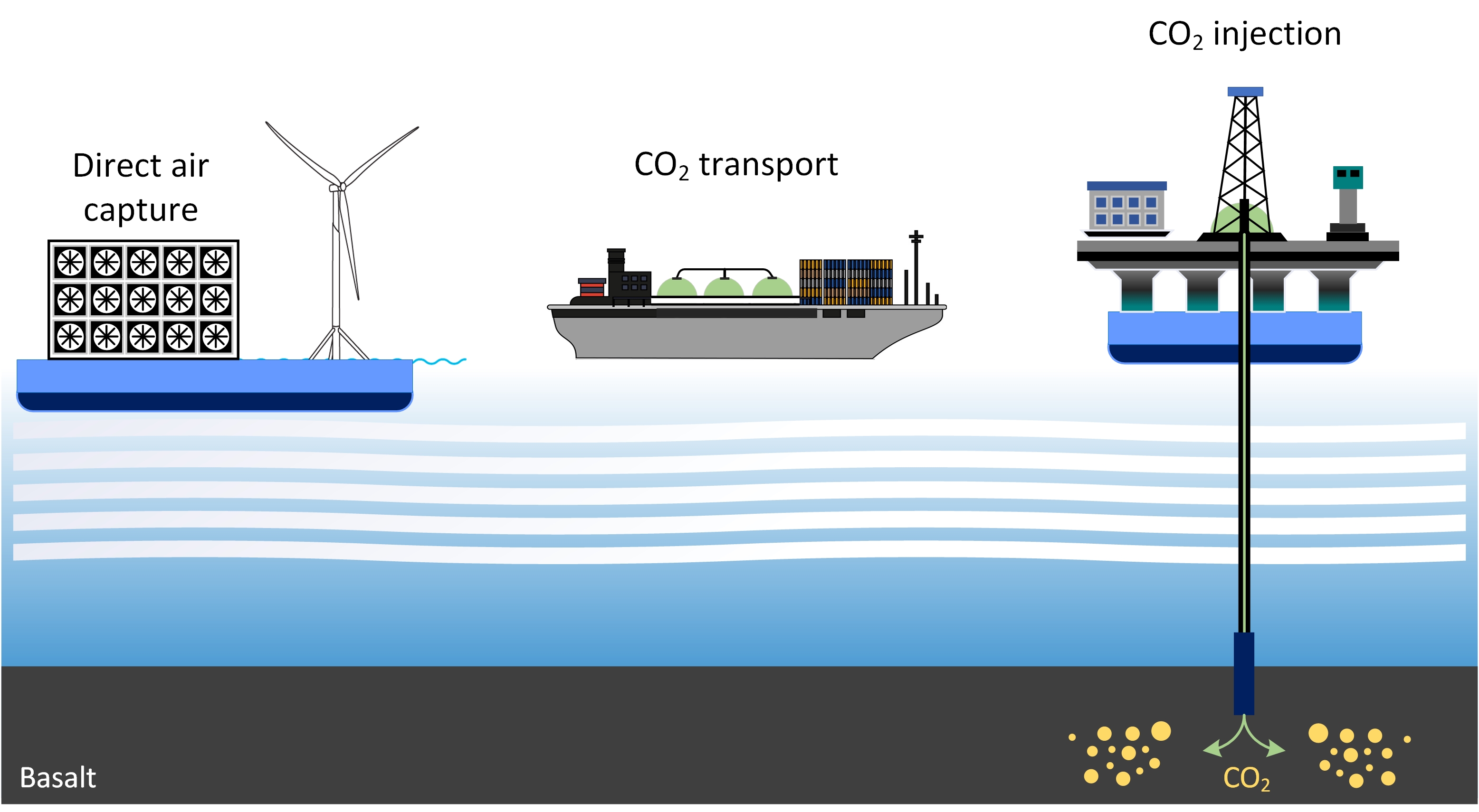

The world is setting aggressive targets for climate change mitigation and most pathways require negative emission technologies (NETs) to meet these targets. Direct air capture (DAC) is a promising NET that captures carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmospheric air. Solid Carbon is an ambitious project aiming to capture carbon dioxide out of the atmospheric air using enormous offshore wind technical potential and store captured CO2 in deep-sea basalt rocks where CO2 mineralizes and converts into solid carbon rock over time. Research topics include techno-economic optimization and design of offshore capture and storage systems along with broader applications of offshore wind to carbon capture storage (CCS), carbon capture, utilization and storage (CCUS), electrochemical direct air capture and production of zero-carbon (H2 and NH3) and synthetic fuels.
This project is currently funded in partnership with PICS, and gratefully acknowledges an anonymous donor that has enabled expanded scope beyond the PICS Solid Carbon project. The team has also engaged numerous DAC OEMs, offshore services and wind energy developers and other partners in advancing the concepts toward experimental prototype and demonstration phases.
Impact Investing Hub
 The Impact Investing Hub (formerly VI3Hub) is a research and education hub at the intersection of climate action and impact investing. The hub aims to accelerate capital investments to support the transition to a net zero inclusive economy aligned with the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and the Paris Agreement. Founded by Dr. Basma Majerbi from Gustavson school of Business with support from IESVic and other units on campus, the hub acts as a collaboration platform leveraging expertise from academia, industry, community, financial actors, and policymakers to co-create innovative finance solutions and remove capital gaps to accelerate the net zero transition in BC and beyond.
The Impact Investing Hub (formerly VI3Hub) is a research and education hub at the intersection of climate action and impact investing. The hub aims to accelerate capital investments to support the transition to a net zero inclusive economy aligned with the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and the Paris Agreement. Founded by Dr. Basma Majerbi from Gustavson school of Business with support from IESVic and other units on campus, the hub acts as a collaboration platform leveraging expertise from academia, industry, community, financial actors, and policymakers to co-create innovative finance solutions and remove capital gaps to accelerate the net zero transition in BC and beyond.
2060 Project
The 2060 project plays a key role in examining potential impacts of integration on large-scale energy systems in Canada under various carbon policies and global growth scenarios. The project produces knowledge that can be used effectively by policymakers, academics, industry and others to shape programs to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
IESVic-CESAP

The IESVic Clean Energy Systems Accelerator Program, or IESVIC-CESAP, provides technical advice and services to small and medium sized Canadian companies, and assist in the development of technologies, processes, and services related to clean energy systems. Potential research areas include: wave energy system development, water treatment, building energy optimization, risk and resilience analysis, battery system characterization, wind and tidal energy technology, E-bike development, industrial energy efficiency, energy efficient thermal systems, thermal optimization and design.
For more information contact iesvic.admin@uvic.ca.
photo credit: Desmond1234 (cropped)




